Part 8: Operating principles of fixings
 |
|||||
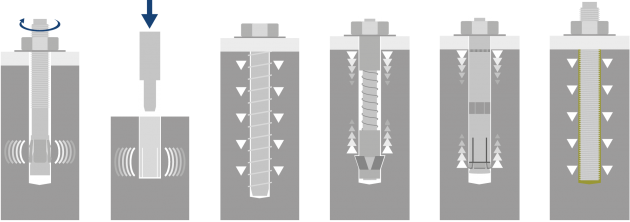
| Through bolts, PFG-anchors | Drop in anchors | Screw anchors | Undercut anchors | Self-undercutting anchors | Injection resins |
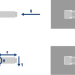
| Friction locking
When tightened, the expanding part of the fastener is pressed against the wall of the drill hole |
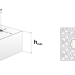
Form locking
The shape of the fastener fits in the of a drill hole or when clamped, the fastener cuts into the mounting base |
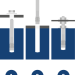
Chemical locking
a chemical mass or resin attaches the selected fastener to the substrate.
|
|||